5 ways 5G will transform healthcare
Improving patient experience with personalized, preventative care
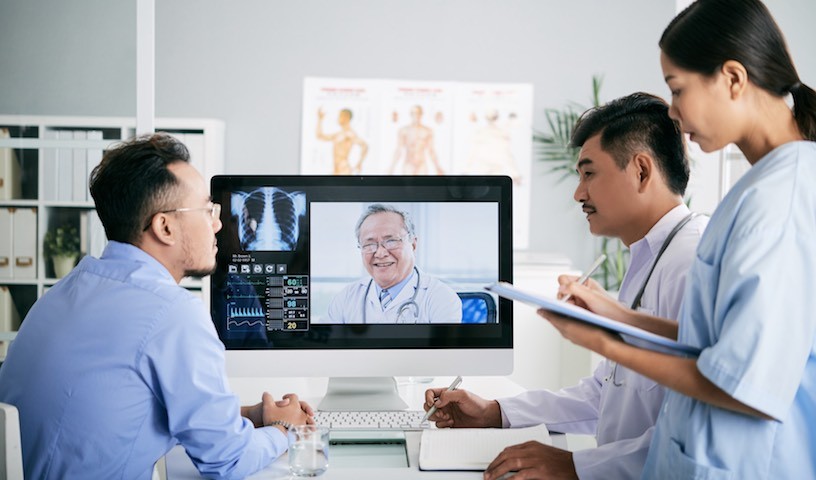
In most cases, we used to only have one option when we became ill and needed medical attention: travel to a doctor or hospital.
For people in rural areas, with doctors located several miles away, traveling while ill can be challenging and time-consuming. With the advent of telehealth and remote home monitoring systems, though, we could receive care from the comfort of our homes. Doctors could make recommendations after a short video call, and even submit prescription requests.
However, this remote monitoring, along with sophisticated imaging equipment, can lead to additional strain on the networks of businesses in the healthcare industry. This often increases congestion and slows network speeds, especially for healthcare providers that might be interfacing with dozens of patients a day.
The lag is not only frustrating for those using it, but the poor quality can delay patient care, which could hurt outcomes in the long run. And because the use of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies continue to grow, the amount of data on networks is expected to only increase more.
5G technologies have the potential to help resolve these challenges. Here are five ways 5G can help healthcare organizations meet the growing demands of digital transformation.

5G & Healthcare: the future is now
5G, the fifth generation of cellular wireless technology, will offer massive connection power and fast speeds that can help transform how healthcare is delivered. Download this free eBook to learn more about this exciting new technology and how to prepare your organization.
1. Quickly transmitting large imaging files
MRIs and other image machines are typically very large files, and often must be sent to a specialist for review. When the network is low on bandwidth, the transmission can take a long time or not send successfully. This means the patient waits even longer for treatment and providers can see fewer patients in the same amount of time.
Adding a high-speed 5G network to existing architectures can help quickly and reliably transport huge data files of medical imagery, which can improve both access to care and the quality of care. At the Austin Cancer Center, the PET scanner generates extremely large files — up to 1 gigabyte of information per patient per study.
“To get that much data from one side of the town to another, you’ve got to have the network performance to handle it,” says Jason Lindgren, CIO of Austin Cancer Center. “We used to have to send the files after hours. Now as soon as the patient leaves the scanner, the study is already on its way. It’s beneficial to doctors because they can get the results that they need quicker.”
2. Expanding telemedicine
According to a study by Market Research Future, the telemedicine market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 16.5% from 2017 to 2023. The study determined that the reason for the predicted increase is demand in rural areas for healthcare, as well as a rise in government initiatives.
Telemedicine requires a network that can support real-time high-quality video, which often means wired networks. With 5G, healthcare systems can enable mobile networks to handle telemedicine appointments, which can greatly increase the reach of the program.
When healthcare systems utilize this technology, patients can often get treated sooner and have access to specialists otherwise not available. It can also allow doctors and other staff members to collaborate more efficiently.
Now as soon as the patient leaves the scanner, the study is already on its way.Share this quote
3. Improving AR, VR and spatial computing
While augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and spatial computing are already being used in healthcare on a limited basis, 5G may eventually further enhance a doctor's ability to deliver innovative, less invasive treatments. Among 5G’s many ultimate potential applications, some of the most exciting involve its role in simulating complex medical scenarios and enabling alternative treatments for the critically ill.
AT&T is working at the forefront of this exciting field, exploring opportunities to apply 5G to medical challenges. AT&T is collaborating with VITAS® Healthcare to study the effects of eventual 5G-enabled AR and VR on patient engagement. The goal is to reduce pain and anxiety for terminally ill patients in hospice by providing calming, distracting content via 5G-enabled AR and VR.
4. Reliable, real-time remote monitoring
By using IoT devices, healthcare providers can monitor patients and gather data that can be used to improve personalized and preventive care.
According to Anthem, 86% of doctors say wearables, which are a common type of remote monitoring, increase patient engagement with their own health. Additionally, wearables are predicted to decrease hospital costs by 16% in the next five years.
Despite the benefits, remote monitoring technology usage is limited by the capacity of the network to handle the data. Slow network speeds and unreliable connections could mean doctors are unable to get the real-time data they need to make quick healthcare decisions.
With 5G technology, which has lower latency and higher capacity, healthcare systems can offer remote monitoring for more patients. Providers can then be confident that they will receive the data they need in real time and can provide the care their patients need and expect.
With 5G, translators can video conference with the patient and doctor using models at the network edge with low latency.Share this quote
5. Artificial intelligence
Many key healthcare functions are beginning to use artificial intelligence (AI) to determine potential diagnoses and decide on the best treatment plan for a specific patient. Additionally, AI can help predict which patients are more likely to have post-operative complications, allowing healthcare systems to provide early interventions when necessary.
The large amounts of data needed for real-time rapid learning require ultra-reliable and high-bandwidth networks. Additionally, providers often need to access data from their mobile devices.
By moving to 5G networks, healthcare organizations can use the AI tools they need to provide the best care possible – from wherever they are in the hospital or clinic.
Preparing for change
By enabling all these technologies through 5G networks, healthcare systems can improve the quality of care and patient experience, reduce the cost of care, and more.
Instead of only reacting to patients' conditions, 5G networks can give providers the ability to provide more personalized and preventive care – which is the reason many healthcare employees became providers in the first place.
Visit our healthcare solutions page to learn more about how your business can embrace next-generation technologies.
Share
Share this with others